2015MBA/MPA/MEM/MPAcc管理类专业硕士联考英语真题
时间:2014-12-29 12:06来源:未知 作者:立仁东方
立仁东方MBA第一时间发布2015MBA/MEM等管理类专业硕士联考英语真题
2015MBA/MBA/MEM/MPAcc管理类专业硕士联考英语真题
Section I Use of English
Directions:
Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on the ANSWER SHEET. (10 points)
In our contemporary culture, the prospect of communicating with – or even looking at – a
stranger is virtually unbearable. Everyone around us seems to agree by the way they cling to the
phones, even without a __1__ on a subway.
It’s a sad reality – our desire to avoid interacting with other human beings – because there’s __2__ to be gained from talking to the stranger standing by you. But you wouldn’t know it, __3__into your phone. This universal protection sends the __4__:”Please don’t approach me.” What is it that makes us feel we need to hide __5__ our screens?
One answer is fear, according to Jon Wortmann, an executive mental coach. We fear rejection,
or that our innocent social advances will be __6__ as “weird.”We fear we’ll be __7__. We fear
we’ll be disruptive.
Strangers are inherently__8__to us, so we are more likely to feel__9__when communicating
with them compared with our friends and acquaintances. To avoid this uneasiness, we_ 10_ to our
phones.” Phones become our security blanket,” Wortmann says.”They are our happy glasses that
protect us from what we perceive is going to be more __11___” But once we rip off the band-aid, tuck our smartphones in our pockets and look up, it doesn’t ___12___so bad. In one 2011 experiment, behavioral scientists Nicholas Epley and Juliana
Schroeder asked commuters to do the unthinkable: Start a __13___. They had Chicago train
commuters talk to their fellow __14___.”When Dr. Epley and Ms.Schroeder asked other people in
the same train station to __15___how they would feel after talking to a stranger, the commuters
thought their __16___ would be more pleasant if they sat on their own,” The New York Times
summarizes. Though the participants didn’t expect a positive experience, after they __17__with
the experiment,” not a single person reported having been embarrassed” __18__, these commutes were reportedly more enjoyable compared with those without
communication, which makes absolute sense, ___19___human beings thrive off of social
connections. It’s that ___20___: Talking to strangers can make you feel connected.
1. [A]signal [B]permit [C]ticket [D]record
2. [A]nothing [B]little [C]another [D]much
3. [A]beaten [B]guided [C]plugged [D]brought
4. [A]sign [B]code [C]notice [D]message
5. [A]under [B]behind [C]beyond [D]from
6. [A]misapplied [B]mismatched [C]misadjusted [D]misinterpreted
7. [A]replaced [B]fired [C]judged [D]delayed
8. [A]unreasonable [B]ungrateful [C]unconventional [D]unfamiliar
9. [A]comfortable [B]confident [C]anxious [D]angry
10. [A]attend [B]point [C]take [D]turn
11. [A]dangerous [B]mysterious [C]violent [D]boring
12. [A]hurt [B]resist [C]bend [D]decay
13. [A]lecture [B]conversation [C]debate [D]negotiation
14. [A]passengers [B]employees [C]researchers [D]trainees
15. [A]reveal [B]choose [C]predict [D]design
16. [A]voyage [B]ride [C]walk [D]flight
17. [A]went through [B]did away [C]caught up [D]put up
18. [A]In turn [B]In fact [C]In particular [D]In consequence
19. [A]unless [B]since [C]if [D]whereas
20. [A]funny [B]logical [C]simple [D]rare
Section II Reading Comprehension
Part A
Directions:
Read the following four texts. Answer the questions after each text by choosing A, B, C or D.
Mark your answers on the ANSWER SHEET. (40 points)
home that at work. Researchers measured people's cortisol, which is a stress marker, while they
were at word and while they were at home and found it higher at what is supposed to be a place of
refuge.
"Further contradicting conventional wisdom, we found that women as well as men have
lower levels of stress at work that at home," writer one of the researchers, Sarah Damaske. In fact
women even say they feel better at work, she notes."It is men, not women, who report being
happier at home that at work." Another surprise is that the findings hold true for both those with
children and without, but more so for nonparents. This is why people who work outside the home
have better health.
What the study doesn't measure is whether people are still doing work when they're at home, whether it is household work or work brought home from the office. For many men, the end of the workday is a time to kick back. For women who stay home, they never get to leave the office. And
for women who work outside the home, they often are playing catch-up-with-household tasks.
With the blurring of roles, and the fact that the home front lags well behind the workplace in
making adjustments for working women it's not surprising that women are more stressed at home.
But it's not just a gender thing. At work, people pretty much know what they're supposed to be doing to be doing: wording, making money, doing the tasks they have to do in order to draw an
income. The bargain is very pure: Employee puts in hours of physical or mental labor and employee draws out life-sustaining moola.
On the home front, however, people have no such clarity. Rare is the household in which the division of labor is so clinically and methodically laid out. There are a lot of tasks to be done, there are inadequate rewards for most of them. Your home colleagues-your family-have no clear rewards for their labor; they need to be talked into is, of if they're teenagers, threatened with complete removal of all electronic devices. Plus, they’re teenagers, threatened with complete removal of all electronic devices. Plus, they're your family. You cannot fire your family. You never really get to go home from home.
So it's not surprising that people are more stressed at home. Not only are the tasks apparently infinite, the co-workers are much harder to motivate.
21. According to Paragraph 1, most previous surveys found that home________.
[A] offered greater relaxation than the workplace
[B] was an ideal place for stress measurement
[C] generated more stress than the workplace
[D] was an unrealistic place for relaxation
22. According to Damaske, who are likely to be the happiest at home?
[A] Childless wives
[B] working mothers
[C] Childless husbands
[D] Working fathers
23. The blurring of working women’s roles refers to the fact that____
[AJ it is difficult for them to leave their office
{B] their home is also a place for kicking back
[C] there is often much housework left behind
[DJ they are both bread winners and housewives
24. The word "moola"(Line 4, para.4) most probably means____
[A]skills
[B]energy
[C]earnings
[D]nutrition
25. The home front differs from the workplace in that_____
[A]division of labor at home is seldom clear-cut
[B]home is hardly a cozier working environment
[C]household tasks are generally more motivating
[D]family labor is often adequately rewarded
grades are lower and their dropout rates are higher. But since such students are most likely to
advance economically if they succeed in higher education, colleges and universities have pushed
for decades to recruit more of them. This has created "a paradox" in that recruiting first-generation
students, but then watching many of them fail, means that higher education has "continued to
reproduce and widen, rather than close" an achievement gap based on social class, according to
the depressing beginning of a paper forthcoming in the journal Psychological Science.
But the article is actually quite optimistic, as it outlines a potential solution to this problem,
suggesting that an approach (which involves a one-hour, next-to-no-cost program) can close 63
percent of the achievement gap (measured by such factors as grades) between first-generation and
other students.
The authors of the paper are from different universities, and their findings are based on a
study involving 147 students (who completed the project) at an unnamed private university. First
generation was defined as not having a parent with a four-year college degree. Most of the
first-generation students (59.1 percent) were recipients of Pell Grants, a federal grant for
undergraduates with financial need, while this was true only for 8.6 percent of the students with at
least one parent with a four-year degree.
Their thesis-that a relatively modest intervention could have a big impact-was based on the
view that first-generation students may be most lacking not in potential but in practical knowledge
about how to deal with the issues that face most college students. They cite past research by several authors to show that this is the gap that must be narrowed to close the achievement gap.
Many first-generation students "struggle to navigate the middle-class culture of higher
education, learn the 'rules of the game,' and take advantage of colleges resources,” they write, And this becomes more of a problem when colleges don't talk about the class advantages and disadvantages of different groups of students."Because US colleges and universities seldom acknowledge how social class can affect students' educational experiences, many first-generation
students lack insight about why they are struggling and do not understand how students "like
them' can improve."
26. Recruiting more first-generation students has .
[A] reduced their dropout rates
[B] narrowed the achievement gap
[C] depressed college students
[D] missed its original purpose
27. The authors of the research article are optimistic because .
[A] their findings appeal to students
[B] the recruiting rate has increased
[C] the problem is solvable
[D] their approach is costless
28. The study suggests that most first-generation students .
[A] study at private universities
[B] are from single-parent families
[C] are in need of financial support
[D] have failed their college
29. The authors of the paper believe that first-generation students .
[A] are actually indifferent to the achievement gap
[B] can have a potential influence on other students
[C] may lack opportunities to apply for research projects
[D] are inexperienced in handling their issues at college
30. We may infer from the last paragraph that .
[A] universities often reject the culture of the middle-class
[B] colleges are partly responsible for the problem in question
[C] social class greatly helps enrich educational experiences
[D] students are usually to blame for their lack of resources
31. According to Nancy Koehn, office language has become_______.
[A]more objective
[B]less energetic
[C]more emotional
[D]less strategic
32."Team"-oriented corporate vocabulary is closely related to_______.
[A]sports culture
[B]gender difference
[C]historical incidents
[D]athletic executives
33. Khurana believes that the importation of terminology aims to______.
[A]promote company image
[B]strengthen employee loyalty
[C]foster corporate cooperation
[D]revive historical terms
34. It can be inferred that Lean In______.
[A]voices for working women
[B]appeals to passionate workaholics
[C]triggers debates among mommies
[D]praises motivated employees
35. Which of the following statements is true about office speak?
[A]Managers admire it but avoid it.
[B]Linguists believe it to be nonsense.
[C]Companies find it to be fundamental.
[D]Regular people mock it but accept it.
with the drop in the unemployment rate to 6.1 percent, as good news. And they were right. For
now it appears the economy is creating jobs at a least we are now finally moving forward at a
faster pace.
However, there is another important part of the jobs picture that was largely overlooked.
There was a big jump in the number of people who report voluntarily working part-time. This
figure is now 830,000(4.4 percent) above its year ago level.
Before explaining the connection to the Obamacare, it is worth making an important
distinction. Many people who work part-time jobs actually want full-time jobs. They take
part-time work because this is all they can get. An increase in involuntary part-time work is
evidence of weakness in the labor market and it means that many people will be having a very
hard time making ends meet.
There was an increase in involuntary part-time in June, but the general direction has been
down. Involuntary part-time employment is still far higher than before the recession, but it is
down by 640,000(7.9 percent) from its year ago level.
We know the difference between voluntary and involuntary part-time employment because
people tell us. The survey used by the Labor Department asks people if they worked less than 35
hours in the reference week. If the answer is “yes”, they are classified as working part-time. The
survey then asks whether they worked less than 35 hours in that week because they wanted to
work less than full time or because they had no choice. They are only classified as voluntary
part-time workers if they tell the survey taker they chose to work less than 35 hours a week.
The issue of voluntary part-time relates to Obamacare because one of the main purposes was
to allow people to get insurance outside of employment. For many people, especially those with
serious health conditions or family members with serious health conditions, before Obamacare the
only way to get insurance was through a job that provided health insurance.
However, Obamacare has allowed more than 12 million people to either get insurance
through Medicaid or the exchanges. These are people who may previously have felt the need toget a full-time job that provided insurance in order to cover themselves and their families. With
Obamacare there is no longer a link between employment and insurance.
36. Which part of the jobs picture was neglected?
[A]The prospect of a thriving job market.
[B]The increase of voluntary part-time jobs.
[C]The possibility of full employment.
[D]The acceleration of job creation.
37. Many people work part-time because they ____.
[A]Fell that is enough to make ends meet
[B]Cannot get their hands on full-time jobs
[C]Haven’t seen the weakness of the market
[D]Prefer part-time jobs to full-time jobs
38. Involuntary part-time employment in the US______.
[A]Shows a general tendency of decline
[B]Is harder to acquire than one year ago
[C]Satisfies the real need of the jobless
[D]Is lower than before the recession
39. It can be learned that with Obamacare, ___ .
[A]It is no longer easy for part-timers to get insurance
[B]Employment is no longer a precondition to get insurance
[C]It is still challenging to get insurance for family members
[D]Full-time employment is still essential for insurance
40. The text mainly discusses_______.
[A]Obamacare’s trouble
[B]Part-timer classification
[C]Insurance through Medicaid
[D]Employment in the US
Read the following text and answer the questions by choosing the most suitable subheading from
the list A-G for each numbered paragraph (41-45).There are two extra subheadings which you do
not need to use. Mark your answers on the ANSWER SHEET. (10 points)
[A]You are not alone
[B]Don’t fear responsibility for your life
[C]Pave your own unique path
[D]Most of your fears are unreal
[E]Think about the present moment
[F]Experience helps you grow
[G]There are many things to be grateful for
Some Old Truths to Help You Overcome Tough Times
Unfortunately, life is not a bed of roses, We are going though life facing sad experiences.
Moreover, we are grieving various kinds of loss: a friendship, a romantic relationship or a house .Hard times may hold you down at what usually seems like the most inopportune time, but you should remember that they won’t last forever.
When our time of mourning is over, we press forward, stronger with a greater understanding
and respect for life. Furthermore, these losses make us mature and eventually move us toward
future opportunities for growth and happiness. I want to share these old truths I’ve learned along
the way.
41________________________
Fear is both useful and harmful. This normal human reaction is used to protect us by
signaling danger and preparing us to deal with it. Unfortunately, people create inner barriers with a help of exaggerating fears. My favorite actor Will Smith once said, “Fear is not real. It is a product
of thoughts you create. Do not misunderstand me. Danger is very real. But fear is a choice. ” I do
completely agree the fears are just the product of our luxuriant imagination.
42.
If you are surrounded by problems and cannot stop thinking about the past, try focus on the
present moment. Many of us are weighed down by the past or anxious about the future. You may
feel guilt over your past, but you are poisoning the present with the things and circumstances you
cannot change. Value the present moment and remember how fortunate you are to be alive. Enjoy
the beauty of the world around and keep the eyes open to see the possibilities before you.
Happiness is not a point of future and not a moment from the past, but a mindset that can be
designed into the present.
43.
Sometimes it is easy to feel bad because you are going through tough times. You can be easily
caught up by life problems that you forget to pause and appreciate the things you have. Only
strong people prefer to smile and value their life instead of crying and complaining about
something.
44.
No matter how isolated you might feel and how serious the situation is, you should always
remember that you are not alone. Try to keep in mind that almost everyone respects and wants to
help you if you are trying to make a good change in your life. Especially your dearest and nearest
people. You may have a circle of friends who provide constant good humor, help and
companionship. If you have no friends or relatives, try to participate in several online communities,
full of people who are always willing to share advice and encouragement.
45.
Today many people find it difficult to trust their own opinion and seek balance by gaining
objectivity from external sources. This way you devalue your opinion and show that you are
incapable of managing your own life. When you are struggling to achieve something important
you should believe in yourself and be sure that your decision is the best. You live in your skin,
think your own thoughts, have your own values and make your own choices.
Section IV Writing
Part A
47. Directions:
Suppose your university is going to bost a summer camp for high school students. Write a notice t
1) briefly introduce the camp activities, and
2) call for volunteers.
You should write about 100 words on the ANSWER SHEET
Do not use your name or the name of your university.
Do not write your address. (10 points)
Part B
48. Directions:
Write an essay based on the following chart. In your writing, you should
1) interpret the chart, and
2) give your comments.
You should write about 150 words on the ANSWER SHEET. (15 points)

2015MBA/MBA/MEM/MPAcc管理类专业硕士联考英语真题
Section I Use of English
Directions:
Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on the ANSWER SHEET. (10 points)
In our contemporary culture, the prospect of communicating with – or even looking at – a
stranger is virtually unbearable. Everyone around us seems to agree by the way they cling to the
phones, even without a __1__ on a subway.
It’s a sad reality – our desire to avoid interacting with other human beings – because there’s __2__ to be gained from talking to the stranger standing by you. But you wouldn’t know it, __3__into your phone. This universal protection sends the __4__:”Please don’t approach me.” What is it that makes us feel we need to hide __5__ our screens?
One answer is fear, according to Jon Wortmann, an executive mental coach. We fear rejection,
or that our innocent social advances will be __6__ as “weird.”We fear we’ll be __7__. We fear
we’ll be disruptive.
Strangers are inherently__8__to us, so we are more likely to feel__9__when communicating
with them compared with our friends and acquaintances. To avoid this uneasiness, we_ 10_ to our
phones.” Phones become our security blanket,” Wortmann says.”They are our happy glasses that
protect us from what we perceive is going to be more __11___” But once we rip off the band-aid, tuck our smartphones in our pockets and look up, it doesn’t ___12___so bad. In one 2011 experiment, behavioral scientists Nicholas Epley and Juliana
Schroeder asked commuters to do the unthinkable: Start a __13___. They had Chicago train
commuters talk to their fellow __14___.”When Dr. Epley and Ms.Schroeder asked other people in
the same train station to __15___how they would feel after talking to a stranger, the commuters
thought their __16___ would be more pleasant if they sat on their own,” The New York Times
summarizes. Though the participants didn’t expect a positive experience, after they __17__with
the experiment,” not a single person reported having been embarrassed” __18__, these commutes were reportedly more enjoyable compared with those without
communication, which makes absolute sense, ___19___human beings thrive off of social
connections. It’s that ___20___: Talking to strangers can make you feel connected.
1. [A]signal [B]permit [C]ticket [D]record
2. [A]nothing [B]little [C]another [D]much
3. [A]beaten [B]guided [C]plugged [D]brought
4. [A]sign [B]code [C]notice [D]message
5. [A]under [B]behind [C]beyond [D]from
6. [A]misapplied [B]mismatched [C]misadjusted [D]misinterpreted
7. [A]replaced [B]fired [C]judged [D]delayed
8. [A]unreasonable [B]ungrateful [C]unconventional [D]unfamiliar
9. [A]comfortable [B]confident [C]anxious [D]angry
10. [A]attend [B]point [C]take [D]turn
11. [A]dangerous [B]mysterious [C]violent [D]boring
12. [A]hurt [B]resist [C]bend [D]decay
13. [A]lecture [B]conversation [C]debate [D]negotiation
14. [A]passengers [B]employees [C]researchers [D]trainees
15. [A]reveal [B]choose [C]predict [D]design
16. [A]voyage [B]ride [C]walk [D]flight
17. [A]went through [B]did away [C]caught up [D]put up
18. [A]In turn [B]In fact [C]In particular [D]In consequence
19. [A]unless [B]since [C]if [D]whereas
20. [A]funny [B]logical [C]simple [D]rare
Section II Reading Comprehension
Part A
Directions:
Read the following four texts. Answer the questions after each text by choosing A, B, C or D.
Mark your answers on the ANSWER SHEET. (40 points)
Text1
A new study suggests that contrary to most surveys, people are actually more stressed athome that at work. Researchers measured people's cortisol, which is a stress marker, while they
were at word and while they were at home and found it higher at what is supposed to be a place of
refuge.
"Further contradicting conventional wisdom, we found that women as well as men have
lower levels of stress at work that at home," writer one of the researchers, Sarah Damaske. In fact
women even say they feel better at work, she notes."It is men, not women, who report being
happier at home that at work." Another surprise is that the findings hold true for both those with
children and without, but more so for nonparents. This is why people who work outside the home
have better health.
What the study doesn't measure is whether people are still doing work when they're at home, whether it is household work or work brought home from the office. For many men, the end of the workday is a time to kick back. For women who stay home, they never get to leave the office. And
for women who work outside the home, they often are playing catch-up-with-household tasks.
With the blurring of roles, and the fact that the home front lags well behind the workplace in
making adjustments for working women it's not surprising that women are more stressed at home.
But it's not just a gender thing. At work, people pretty much know what they're supposed to be doing to be doing: wording, making money, doing the tasks they have to do in order to draw an
income. The bargain is very pure: Employee puts in hours of physical or mental labor and employee draws out life-sustaining moola.
On the home front, however, people have no such clarity. Rare is the household in which the division of labor is so clinically and methodically laid out. There are a lot of tasks to be done, there are inadequate rewards for most of them. Your home colleagues-your family-have no clear rewards for their labor; they need to be talked into is, of if they're teenagers, threatened with complete removal of all electronic devices. Plus, they’re teenagers, threatened with complete removal of all electronic devices. Plus, they're your family. You cannot fire your family. You never really get to go home from home.
So it's not surprising that people are more stressed at home. Not only are the tasks apparently infinite, the co-workers are much harder to motivate.
21. According to Paragraph 1, most previous surveys found that home________.
[A] offered greater relaxation than the workplace
[B] was an ideal place for stress measurement
[C] generated more stress than the workplace
[D] was an unrealistic place for relaxation
22. According to Damaske, who are likely to be the happiest at home?
[A] Childless wives
[B] working mothers
[C] Childless husbands
[D] Working fathers
23. The blurring of working women’s roles refers to the fact that____
[AJ it is difficult for them to leave their office
{B] their home is also a place for kicking back
[C] there is often much housework left behind
[DJ they are both bread winners and housewives
24. The word "moola"(Line 4, para.4) most probably means____
[A]skills
[B]energy
[C]earnings
[D]nutrition
25. The home front differs from the workplace in that_____
[A]division of labor at home is seldom clear-cut
[B]home is hardly a cozier working environment
[C]household tasks are generally more motivating
[D]family labor is often adequately rewarded
Text2
For years, studies have found that first-generation collage students-those who do not have a parent with a college degree-lag other students on a range of education achievement factors. Theirgrades are lower and their dropout rates are higher. But since such students are most likely to
advance economically if they succeed in higher education, colleges and universities have pushed
for decades to recruit more of them. This has created "a paradox" in that recruiting first-generation
students, but then watching many of them fail, means that higher education has "continued to
reproduce and widen, rather than close" an achievement gap based on social class, according to
the depressing beginning of a paper forthcoming in the journal Psychological Science.
But the article is actually quite optimistic, as it outlines a potential solution to this problem,
suggesting that an approach (which involves a one-hour, next-to-no-cost program) can close 63
percent of the achievement gap (measured by such factors as grades) between first-generation and
other students.
The authors of the paper are from different universities, and their findings are based on a
study involving 147 students (who completed the project) at an unnamed private university. First
generation was defined as not having a parent with a four-year college degree. Most of the
first-generation students (59.1 percent) were recipients of Pell Grants, a federal grant for
undergraduates with financial need, while this was true only for 8.6 percent of the students with at
least one parent with a four-year degree.
Their thesis-that a relatively modest intervention could have a big impact-was based on the
view that first-generation students may be most lacking not in potential but in practical knowledge
about how to deal with the issues that face most college students. They cite past research by several authors to show that this is the gap that must be narrowed to close the achievement gap.
Many first-generation students "struggle to navigate the middle-class culture of higher
education, learn the 'rules of the game,' and take advantage of colleges resources,” they write, And this becomes more of a problem when colleges don't talk about the class advantages and disadvantages of different groups of students."Because US colleges and universities seldom acknowledge how social class can affect students' educational experiences, many first-generation
students lack insight about why they are struggling and do not understand how students "like
them' can improve."
26. Recruiting more first-generation students has .
[A] reduced their dropout rates
[B] narrowed the achievement gap
[C] depressed college students
[D] missed its original purpose
27. The authors of the research article are optimistic because .
[A] their findings appeal to students
[B] the recruiting rate has increased
[C] the problem is solvable
[D] their approach is costless
28. The study suggests that most first-generation students .
[A] study at private universities
[B] are from single-parent families
[C] are in need of financial support
[D] have failed their college
29. The authors of the paper believe that first-generation students .
[A] are actually indifferent to the achievement gap
[B] can have a potential influence on other students
[C] may lack opportunities to apply for research projects
[D] are inexperienced in handling their issues at college
30. We may infer from the last paragraph that .
[A] universities often reject the culture of the middle-class
[B] colleges are partly responsible for the problem in question
[C] social class greatly helps enrich educational experiences
[D] students are usually to blame for their lack of resources
31. According to Nancy Koehn, office language has become_______.
[A]more objective
[B]less energetic
[C]more emotional
[D]less strategic
32."Team"-oriented corporate vocabulary is closely related to_______.
[A]sports culture
[B]gender difference
[C]historical incidents
[D]athletic executives
33. Khurana believes that the importation of terminology aims to______.
[A]promote company image
[B]strengthen employee loyalty
[C]foster corporate cooperation
[D]revive historical terms
34. It can be inferred that Lean In______.
[A]voices for working women
[B]appeals to passionate workaholics
[C]triggers debates among mommies
[D]praises motivated employees
35. Which of the following statements is true about office speak?
[A]Managers admire it but avoid it.
[B]Linguists believe it to be nonsense.
[C]Companies find it to be fundamental.
[D]Regular people mock it but accept it.
Text 3
Even in traditional offices,” the lingua franca of corporate America has gotten much more emotional and much more right-brained than it was 20 years ago, ” said Harvard Business School professor Nancy Koehn. She stared spinning off examples.”If you and I parachuted back of Fortune 500 companies in 1990, we would see much less frequent use of terms like journey, mission passion. There were goals, there were strategies, there were objectives, but we didn’t talk about energy; we didn’t talk about passion. ”
Koehn pointed out that this new era of corporate vocabulary is very “team”-oriented -and not by coincidence.”Let’s not forget sports-in male-dominated corporate America, it’s still a big deal .It’s not explicitly conscious; it’s the idea that I’m a coach, and you’re my team, and we’re in this together. There are lots and lots of CEOs in very different companies, but most think of themselves as coaches and this is their team and they want to win.”
These terms are also intended to infuse work with meaning-and, as Rakesh Khurana , another professor, points out, increase allegiance to the firm.”You have the importation of terminology that historically used to be associated with non-profit organizations and religious organizations: terms like vision, values, passion, and purpose”, said Khurana.
This new focus on personal fulfillment can help keep employees motivated amid increasingly loud debates over work-life balance. The “mommy wars” of the 1990s are still going on today, prompting arguments about why women have it all and books like Sheryl Sandberg’s Lean In, whose title has buzzword in its own right. Terms like unplug, offline, life-hack, bandwidth, and capacity are all about setting boundaries between the office and the home. But if your work is your” passion”, you’ll be more likely to devote yourself to it, even if that means going home for dinner and then working long after the kids are in bed.
But this seems to be the irony of office speak: Everyone makes fun of it, but managers love it, companies depend on it,and regular people willingly absorb it. As a linguist once said,“You can get people to think it’s nonsense at the same time that you buy into it.” In a workplace that’s fundamentally indifferent to your life and its meaning, office speak can help you figure out how you relate to your work-and how your work defines who you are.
1.According to Nancy Koehn, office language has become _______.
[A]less strategic
[B]less energetic
[C]more objective
[D]more emotional
2.“Team”-oriented corporate vocabulary is closely related to_______.
[A]sports culture
[B]gender difference
[C]historical incidents
[D]athletic executives
3.Khurana believes that the importation of terminology aims to ______.
[A]revive historical terms
[B]promote company image
[C]foster corporate image
[D]strengthen employee loyalty
4.It can be inferred that Lean In _______.
[A]voices for working women
[B]appeals to passionate workaholics
[C]triggers debates among mommies
[D]praises motivated employees
5.Which of the following statements is true about office speak?
[A]Linguists believe it to be nonsense.
[B]Regular people mock it but accept it.
[C]Companies find it to be fundamental.
[D]Managers admire it but avoid it.
Koehn pointed out that this new era of corporate vocabulary is very “team”-oriented -and not by coincidence.”Let’s not forget sports-in male-dominated corporate America, it’s still a big deal .It’s not explicitly conscious; it’s the idea that I’m a coach, and you’re my team, and we’re in this together. There are lots and lots of CEOs in very different companies, but most think of themselves as coaches and this is their team and they want to win.”
These terms are also intended to infuse work with meaning-and, as Rakesh Khurana , another professor, points out, increase allegiance to the firm.”You have the importation of terminology that historically used to be associated with non-profit organizations and religious organizations: terms like vision, values, passion, and purpose”, said Khurana.
This new focus on personal fulfillment can help keep employees motivated amid increasingly loud debates over work-life balance. The “mommy wars” of the 1990s are still going on today, prompting arguments about why women have it all and books like Sheryl Sandberg’s Lean In, whose title has buzzword in its own right. Terms like unplug, offline, life-hack, bandwidth, and capacity are all about setting boundaries between the office and the home. But if your work is your” passion”, you’ll be more likely to devote yourself to it, even if that means going home for dinner and then working long after the kids are in bed.
But this seems to be the irony of office speak: Everyone makes fun of it, but managers love it, companies depend on it,and regular people willingly absorb it. As a linguist once said,“You can get people to think it’s nonsense at the same time that you buy into it.” In a workplace that’s fundamentally indifferent to your life and its meaning, office speak can help you figure out how you relate to your work-and how your work defines who you are.
1.According to Nancy Koehn, office language has become _______.
[A]less strategic
[B]less energetic
[C]more objective
[D]more emotional
2.“Team”-oriented corporate vocabulary is closely related to_______.
[A]sports culture
[B]gender difference
[C]historical incidents
[D]athletic executives
3.Khurana believes that the importation of terminology aims to ______.
[A]revive historical terms
[B]promote company image
[C]foster corporate image
[D]strengthen employee loyalty
4.It can be inferred that Lean In _______.
[A]voices for working women
[B]appeals to passionate workaholics
[C]triggers debates among mommies
[D]praises motivated employees
5.Which of the following statements is true about office speak?
[A]Linguists believe it to be nonsense.
[B]Regular people mock it but accept it.
[C]Companies find it to be fundamental.
[D]Managers admire it but avoid it.
Text 4
Many people talked of the 288,000 new jobs the Labor Department reported for June, alongwith the drop in the unemployment rate to 6.1 percent, as good news. And they were right. For
now it appears the economy is creating jobs at a least we are now finally moving forward at a
faster pace.
However, there is another important part of the jobs picture that was largely overlooked.
There was a big jump in the number of people who report voluntarily working part-time. This
figure is now 830,000(4.4 percent) above its year ago level.
Before explaining the connection to the Obamacare, it is worth making an important
distinction. Many people who work part-time jobs actually want full-time jobs. They take
part-time work because this is all they can get. An increase in involuntary part-time work is
evidence of weakness in the labor market and it means that many people will be having a very
hard time making ends meet.
There was an increase in involuntary part-time in June, but the general direction has been
down. Involuntary part-time employment is still far higher than before the recession, but it is
down by 640,000(7.9 percent) from its year ago level.
We know the difference between voluntary and involuntary part-time employment because
people tell us. The survey used by the Labor Department asks people if they worked less than 35
hours in the reference week. If the answer is “yes”, they are classified as working part-time. The
survey then asks whether they worked less than 35 hours in that week because they wanted to
work less than full time or because they had no choice. They are only classified as voluntary
part-time workers if they tell the survey taker they chose to work less than 35 hours a week.
The issue of voluntary part-time relates to Obamacare because one of the main purposes was
to allow people to get insurance outside of employment. For many people, especially those with
serious health conditions or family members with serious health conditions, before Obamacare the
only way to get insurance was through a job that provided health insurance.
However, Obamacare has allowed more than 12 million people to either get insurance
through Medicaid or the exchanges. These are people who may previously have felt the need toget a full-time job that provided insurance in order to cover themselves and their families. With
Obamacare there is no longer a link between employment and insurance.
36. Which part of the jobs picture was neglected?
[A]The prospect of a thriving job market.
[B]The increase of voluntary part-time jobs.
[C]The possibility of full employment.
[D]The acceleration of job creation.
37. Many people work part-time because they ____.
[A]Fell that is enough to make ends meet
[B]Cannot get their hands on full-time jobs
[C]Haven’t seen the weakness of the market
[D]Prefer part-time jobs to full-time jobs
38. Involuntary part-time employment in the US______.
[A]Shows a general tendency of decline
[B]Is harder to acquire than one year ago
[C]Satisfies the real need of the jobless
[D]Is lower than before the recession
39. It can be learned that with Obamacare, ___ .
[A]It is no longer easy for part-timers to get insurance
[B]Employment is no longer a precondition to get insurance
[C]It is still challenging to get insurance for family members
[D]Full-time employment is still essential for insurance
40. The text mainly discusses_______.
[A]Obamacare’s trouble
[B]Part-timer classification
[C]Insurance through Medicaid
[D]Employment in the US
Part B
Directions:Read the following text and answer the questions by choosing the most suitable subheading from
the list A-G for each numbered paragraph (41-45).There are two extra subheadings which you do
not need to use. Mark your answers on the ANSWER SHEET. (10 points)
[A]You are not alone
[B]Don’t fear responsibility for your life
[C]Pave your own unique path
[D]Most of your fears are unreal
[E]Think about the present moment
[F]Experience helps you grow
[G]There are many things to be grateful for
Some Old Truths to Help You Overcome Tough Times
Unfortunately, life is not a bed of roses, We are going though life facing sad experiences.
Moreover, we are grieving various kinds of loss: a friendship, a romantic relationship or a house .Hard times may hold you down at what usually seems like the most inopportune time, but you should remember that they won’t last forever.
When our time of mourning is over, we press forward, stronger with a greater understanding
and respect for life. Furthermore, these losses make us mature and eventually move us toward
future opportunities for growth and happiness. I want to share these old truths I’ve learned along
the way.
41________________________
Fear is both useful and harmful. This normal human reaction is used to protect us by
signaling danger and preparing us to deal with it. Unfortunately, people create inner barriers with a help of exaggerating fears. My favorite actor Will Smith once said, “Fear is not real. It is a product
of thoughts you create. Do not misunderstand me. Danger is very real. But fear is a choice. ” I do
completely agree the fears are just the product of our luxuriant imagination.
42.
If you are surrounded by problems and cannot stop thinking about the past, try focus on the
present moment. Many of us are weighed down by the past or anxious about the future. You may
feel guilt over your past, but you are poisoning the present with the things and circumstances you
cannot change. Value the present moment and remember how fortunate you are to be alive. Enjoy
the beauty of the world around and keep the eyes open to see the possibilities before you.
Happiness is not a point of future and not a moment from the past, but a mindset that can be
designed into the present.
43.
Sometimes it is easy to feel bad because you are going through tough times. You can be easily
caught up by life problems that you forget to pause and appreciate the things you have. Only
strong people prefer to smile and value their life instead of crying and complaining about
something.
44.
No matter how isolated you might feel and how serious the situation is, you should always
remember that you are not alone. Try to keep in mind that almost everyone respects and wants to
help you if you are trying to make a good change in your life. Especially your dearest and nearest
people. You may have a circle of friends who provide constant good humor, help and
companionship. If you have no friends or relatives, try to participate in several online communities,
full of people who are always willing to share advice and encouragement.
45.
Today many people find it difficult to trust their own opinion and seek balance by gaining
objectivity from external sources. This way you devalue your opinion and show that you are
incapable of managing your own life. When you are struggling to achieve something important
you should believe in yourself and be sure that your decision is the best. You live in your skin,
think your own thoughts, have your own values and make your own choices.
Section IV Writing
Part A
47. Directions:
Suppose your university is going to bost a summer camp for high school students. Write a notice t
1) briefly introduce the camp activities, and
2) call for volunteers.
You should write about 100 words on the ANSWER SHEET
Do not use your name or the name of your university.
Do not write your address. (10 points)
Part B
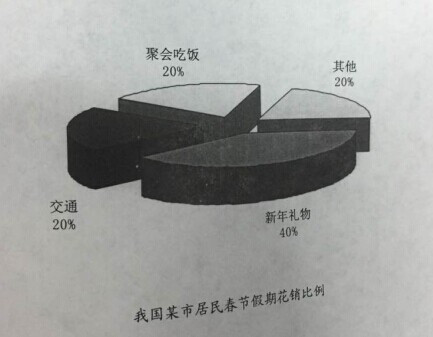
48. Directions:
Write an essay based on the following chart. In your writing, you should
1) interpret the chart, and
2) give your comments.
You should write about 150 words on the ANSWER SHEET. (15 points)






